DEFINITION :
Rheumatic Fever is defined as a delayed inflammatory complication of group A β – hemolytic streptococcal (GAS) Pharyngitis that usually occurs within 2 – 4 weeks of acute infection.
ETIOLOGY :
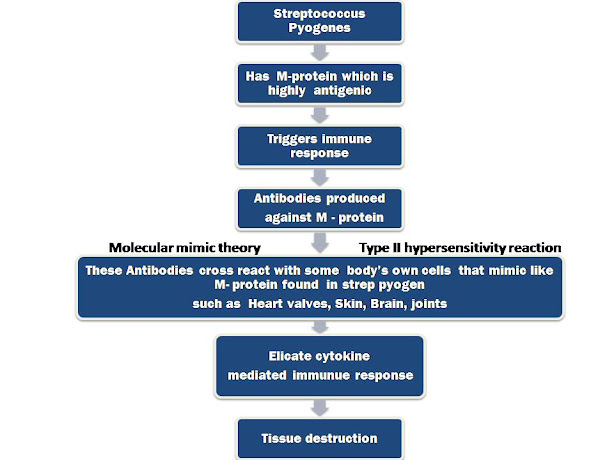
- It is causes by Group A Beta- hemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes ) which cause throat infection.
- If it is untreated it leads to Rheumatic fever as a sequela in some risk peoples
RISK FACTORS :
- Not all peoples suffered from throat infection ( Strep throat ) developes Rheumatic fever
- ~3% patient form Rheumatic fever after strep throat
- there are some risk group they are:
Children are more likely
affected
Peoples in area of Poverty & crowding
EPIDIMIOLOY :
Peak
incidence : 5 – 15 years
TYPES:
1.Acute rheumatic fever :
It leads to Pancarditis as a sequela of GAS (group A beta -hemolytic streptococcus infection
2.Chronic rheumatic fever :
It can lead to chronic valvular changes due to the complications of Acute rheumatic fever
PATHOGENESIS :
CLINICAL FEATURES :
1) Joints – Migratory Polyarthritis
Migratory - One after another
Poly - Multiple
Arthritis - Large joint inflammation
2) heart :
Pancarditis - all three layers of heart inflammation
- Endocarditis - inflammation of endocardium (innerlying)
- Myocarditis – inflammation of myocardium
inflammed
area in myocardial tissue are called ASCHOFF BODY (area of fibrinoid necrosis)
which contain immune cells and ANTISCHKOW CELLS (enlarged macrophages with
caterpillar like cells )
myocarditis
is the leading cause of death in Rheumatic fever because inflammation cause
heart wall unable to contract – heart failure
- Pericarditis – inflammation of outer covering of heart
cause
pain and friction rub
Valvular lesions :
- Mitral valve – 65% of case
Early : Mitral regurgitation or prolapsed
Late : Mitral stenosis
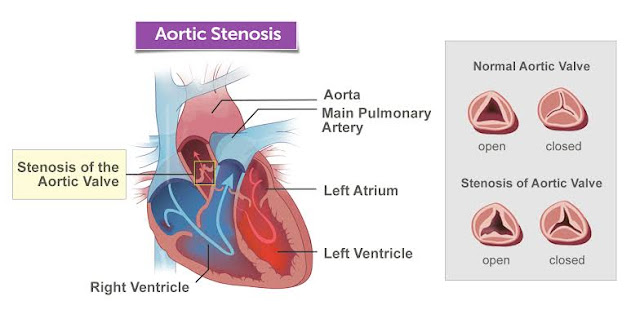
- Aortic valve – 25% of case
Aortic
regurgitation
Aortic
stenosis
- Tricuspid valve - 10%
3) Subcutaneous Nodules :
Firm lump under skin made of collagen
4) Erythema Marginatum :
Reddish rash shows like rings in arms and in trunk
5) Sydenhom chorea
- rapid movements in face & arm
- Due to autoimmune reaction in basal ganglia
- Occurs late atleast 3 months after infection
DIAGNOSIS :
Diagnosis
is based on Jones criteria.
Jones
criteria :
Interpretations
: ( two major or one minor + two minor ) are required for diagnosis.
MAJOR CRITERIA :
- Arthritis – Migratory Polyarthritis
- Carditis – pancarditis, including valvulitis
- Sydenhem chorea – CNS involvement
- Subcutaneous nodules
- Erythema marginatum
- Arthralgia – joint paint
- Fever
- Increased ESR, CRP ( acute phase reactants )
- ECG – prolonged PR interval
TREATMENT:
1) General measures :
bed rest ( especially in patient with carditis )
2 )Antibiotics : to eradicate GAS
Drug of choice : oral penicillin V ( beta lactum antibiotics )
:Alternatives :
Amoxicillin
Benzathine
Cephalosporins
Macrolides
3) Therapy
for arthritis and fever :
NSAIDS
– Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs
Preferred
: salicylates ( eg : asprin )
Childrens
: ibuprofen, naprozen
Glucocorticoids
( if NSAIDS fails )
4) Therapy
for heart failure :
Diuretics
and conventional theraphy
5) Therapy
for myocarditis :
Monitoring
and treatment for arrhythmias ( amiodarone )
6) Damage
to cardiac valves :
Surgery
or interventional reconstructive measures may be considered
atleast
one year after acute inflammatory phase
PROGNOSIS :
Joints – not permentely affected
Heart
– permentently affected
RHEUMATIC FEVER LICKS
THE JOINT
BUT BITES THE HEART
Early
death in rheumatic fever is usually due to myocarditis rather than valvular
defects.
PREVENTION
:
1) Primary
Prevention : Penicillin V
2) Secondary
Prevention :
a. Antibiotics
prophylaxis to prevent recurrence
b. Drug
of choice : 1m Penicillin G benzathine
i.
In patient with Penicillin allergy :
oral marcolides
ii.
Usually administered every 28 days
c. Immediately
follows antibiotic treatment of acute rheumatic fever
d. Duration depends on risk and severity of original episodes
Duration :
Rheumatic fever without carditis :
5 years or until the patient age 21
Rheumatic fever with
carditis :
10 years or until the patient age 21
Rheumatic fever with
carditis and permanent valvular heart defects :
10 years or until age 40
















0 Comments