DEFINITION :
"Parkinson’s Disease is a neuro degenerative disease involving a progressive depletion of dopaminergic neurons in basal ganglia, particularly the Substantia nigra."

Degeneration of neurons in Substantia nigra
 |
| Degeneration of neurons in Substantia nigra |
ETIOLOGY :
1.Parkinson’s
disease – idiopathic
2.Secondary
Parkinsonism – {Parkinsonism or Parkinson syndrome} which may caused by
Medication – which cause antidopinergic effect
- Haloperidol
- Metoclopramide
- Calcium channel blockers – Amiodarone ,
- Valproate
- Lithium
MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro pyridine)
- Illegal drug
- Damages substantia nigra
Toxins
- magnese
- carbon monoxide
- carbon disulfide
Cerebrovascular disease (Vascular Parkinsonism) :
Eg; Subcortical
arterosclerotic encephalopathy
CNS infection
Other degenerative disease
- Dementia with lewy bodies
- Alzheimer disease
- Multiple system Atrophy
Genetics
- Huntingtons disease
- Willsons disease
- Spinocerebellar ataxia
Anoxic brain injury –
injury to the brain due to lack of
oxygen
 |
| Reduced dopamine production in Parkinsin's patient |
EPIDIMIOLOGY :
Normal mechanism :
When you try to lift your arm the signal pass as follows
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PARKINSONISM :
PATHOLOGY :
- A further pathological hallmark of PD is appearence of LEWY BODIES.
- Lewy bodies are abnormal aggregations of protein that develop inside nerve cells, contributing to Parkinson's disease (PD), the Lewy body dementias and some other disorders.
 |
| Photomicrographs of regions of substantia nigra in this Parkinson's patient show Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in various magnifications. |
CLINICAL FEAUTURES :
MOTOR SYMPTOMS
1.Bradykinesia / akinesia :
- Slowness of movement
- Fatigue and decrease in size of repetitive movements
2.Resting tremor :
Pill rolling tremor - it looks like you are trying to roll a pill or another small object between your thumb and index finger.
- Subside with voluntary movement
- increase with stress
3.Rigidity :
Increased and persistent resistance to fast and slow passive joint movement
Note : Resistance only in Fast passive joint movement - SPASTICITY
- COGWHEEL RIGIDITY - Start and stop movements throughout the range of motion of a joint.
- LEAD PIPE RIGIDITY - Sustained resistance throughout the range of motion.
4.Postural instability : tendency to fall
5.Parkinsonisal gait:
- Slow to start walking
- Reduction of arm swing
- Rapid , short stride length (Fastination)
- Impaired balance on turning
TRAP - Tremor , Rigidity , Akinesia and Postural instability
NON MOTOR SYMPTOMS
- Neuropsychiatric features (anexity, depression, apathy, hallucinosis/psychosis), Dementia
- Sleep disturbance
- Hypersomnolence - is a condition where a person experiences significant episodes of sleepiness, even after having 7 hours or more of quality sleep
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint pain
- Sphincter disturbance
- Constipation
- Sexual problem
- Drooling - drop saliva uncontrollably from the mouth
- Weight loss
- reduction in sense of smell
- Microgrophia : Size of handwritting reduced
GENERAL SYMPTOMS
- Hypomimia - a medical sign, is a reduced degree of facial expression.
- Flexed (Stooped) posture
- Soft,rapid,indistinct speach - Dysphonia
- Impaired postural reflexes
DIAGNOSIS :
1.Levodopa challenge test :
- Administration of LEVODOPA
- If it relive symptoms - Patient is affected with PARKINSON'S diseases
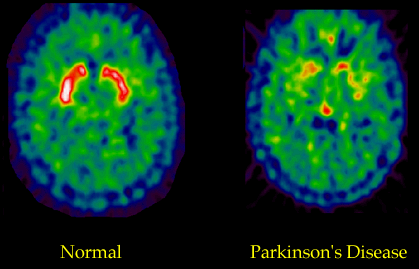
2.Single photon emission CT :
Showed reduced dopamine activity in basal ganglia
TREATMENT :
Aim - to increase dopamine signal in brain
PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT :
1.LEVODOPA + CARBIDOPA -
- Levodopa, the most effective Parkinson's disease medication, is a natural chemical that passes into your brain and is converted to dopamine.
- Levodopa is combined with carbidopa (Lodosyn), which protects levodopa from early conversion to dopamine outside your brain. This prevents or lessens side effects such as nausea.
Side effects : nausea or lightheadedness (orthostatic hypotension).
2.AMANTADINE -
- to provide short-term relief of symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson's disease.
- an Antiviral medication that increase Dopamine production in brain
Side effects: purple mottling of the skin, ankle swelling or hallucinations.
3.DOPAMINE AGONIST -
- Unlike levodopa, dopamine agonists don't change into dopamine. Instead, they mimic dopamine effects in your brain
- there by Stimulate Dopamine receptors in brain
- eg ; Bromocriptine, Pramipexole, Ropinirole
Side effects : hallucinations, sleepiness and compulsive behaviors such as hypersexuality, gambling and eating.
4.MAO B inhibitor (monoamine oxidase-B) inhibitors -
- They help prevent the breakdown of brain dopamine by inhibiting the brain enzyme monoamine oxidase B (MAO B).
- This enzyme metabolizes brain dopamine
- eg ; Selagilline , Rasagiline
Side effects : headaches, nausea or insomnia. When added to carbidopa-levodopa, these medications increase the risk of hallucinations.
5.Catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors -
- Entacapone (Comtan) is the primary medication from this class.
- This medication mildly prolongs the effect of levodopa therapy by blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine.
Side effects : increased risk of involuntary movements (dyskinesia), mainly result from an enhanced levodopa effect. Other side effects include diarrhea, nausea or vomiting.
6.ANTICHOLINERGICS :
- These medications were used for many years to help control the tremor associated with Parkinson's disease
- eg ; benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl.
Side effects : impaired memory, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and impaired urination.
SURGICAL TREATEMENT :
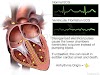
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION :
In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in a specific area of the brain depending on the symptoms being treated. The electrodes are placed on both the left and right sides of the brain through small holes made at the top of the skull. The electrodes are connected by long wires that travel under the skin and down the neck to a battery-powered stimulator under the skin of the chest (Fig. 1). When turned on, the stimulator sends electrical pulses to block the faulty nerve signals causing tremors, rigidity, and other symptoms
 |
Other treatements :
1.Physiotheraphy :
- reduce rigidity
- correct posture
2.Occupational therapist :
Provide equipments to help overcome functional limitations
3.Speach theraphy : for dysarthria, dysphonia








0 Comments